We are Central India’s Largest and First ISO 9001-2008 Certified
Dental and Maxillofacial Surgical Hospital
Meet the Doctors
General Facilities
 Dental X–rays are pictures of the teeth, bones, and soft tissues around them to help find problems with the teeth, mouth, and jaw. X–ray pictures can show cavities, hidden dental structures (such as wisdom teeth), and bone loss that cannot be seen during a visual examination.
Dental X–rays are pictures of the teeth, bones, and soft tissues around them to help find problems with the teeth, mouth, and jaw. X–ray pictures can show cavities, hidden dental structures (such as wisdom teeth), and bone loss that cannot be seen during a visual examination.
There are two main types of dental X-rays: intraoral (meaning the X-ray film is inside the mouth) and extraoral (meaning the X-ray film is outside the mouth).
The benefits of X–rays are well known: They help dentists diagnose common problems, such as cavities, gum disease and some types of infections. Radiographs allow dentists to see inside a tooth and beneath the gums to assess the health of the bone and supporting tissues that hold teeth in place.
 Cosmetic dentistry is done to enhance the esthetics. The various cosmetic dental procedures are:
Cosmetic dentistry is done to enhance the esthetics. The various cosmetic dental procedures are:
- Laminate veneers.
- Bleaching
Laminate veneers:
Laminate veneers are thinly contoured ceramics, which are fixed to the surfaces of the prepared teeth. Laminate veneers are given for
- 1. Spacing in the front teeth
- 2. Discolored teeth
- 3. Fractured teeth
- 4. Malpositioned teeth
The laminate veneers are bonded to the prepared tooth with a special luting agent. Laminate veneers are highly esthetic and durable.
Bleaching:
Bleaching is done to brighten the natural teeth. Bleaching procedure can be done at your home. A custom made bleaching tray is made for your teeth and a bleaching gel is provided to be used at home. Your tooth shade becomes lighter than before.
 Dental pain or tooth related pain is one of the most common cause for which a patient seeks a dentist. Previously common treatment was removal of offending tooth to get relief from pain. But presently the focus of treatment is conservative and not only to relieve from pain but also save the offending tooth.
Dental pain or tooth related pain is one of the most common cause for which a patient seeks a dentist. Previously common treatment was removal of offending tooth to get relief from pain. But presently the focus of treatment is conservative and not only to relieve from pain but also save the offending tooth.
Importance of saving a natural tooth will maintain
a) Esthetic i.e appearance
b) Function- chewing of food
c) Physiology- proper speech or phonation
So we recommend a better and patient friendly treatment, as in long terms a missing tooth will need a replacement so will cost extra financial burden on patient.
The sole purpose of root canal treatment is to remove the infection of tooth and save the tooth.
Common Symptoms requiring an RCT:
- Severe tooth pain, typically relieved by cold water and increases with the intake of hot liquids.
- Pain worsens when you lie down and reduces when you sit up.
- Pain stays for a long time after consuming cold things.
- Swelling around the tooth.
- Constant tooth pain.
- Pain when chewing.
- Tooth pain referred to head and ears as well.
- Deep cavity (carious) in tooth.
- Severe attrition of tooth i.e loss of outer portion of tooth on grinding surface.
- Fractured tooth may be due to trauma.

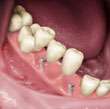 Artificial crowns are given to the natural teeth that have been broken down due to bad decay, extensively damaged , after root canal therapy, fractured or discoloration. Artificial teeth protects the natural tooth from further damage or fracture . The natural teeth are prepared and the impressions of the teeth are made. The impressions are sent to laboratory for further processing. Artificial crowns are custom made in the dental laboratory with CAD CAM TECHNOLOGY and are available in different types of material like
Artificial crowns are given to the natural teeth that have been broken down due to bad decay, extensively damaged , after root canal therapy, fractured or discoloration. Artificial teeth protects the natural tooth from further damage or fracture . The natural teeth are prepared and the impressions of the teeth are made. The impressions are sent to laboratory for further processing. Artificial crowns are custom made in the dental laboratory with CAD CAM TECHNOLOGY and are available in different types of material like
- Cast metal
- Metal ceramic
- All ceramic or metal free ceramic (Zirconia crowns)
Dental Bridges are artificial prosthesis for replacement of missing teeth. A dental bridge takes the support of the adjacent teeth and will be permanently fixed to the natural teeth. The dental bridges can be made in cast metal, metal ceramic and all ceramic or metal free ceramic (Zirconia ) with CAD CAM technology in the dental laboratory. The duration of the treatment will take about 5-7 days and the number of visits will be 2 -4 including the recall visits.
 The purpose of having your teeth cleaned regularly by a trained professional hygienist is to remove deposits of plaque and calculus. Removal of hard deposits on your teeth is called “scaling.” This can be done either by using hand-held scalers or by newer technology: ultrasonic power scalers.
The purpose of having your teeth cleaned regularly by a trained professional hygienist is to remove deposits of plaque and calculus. Removal of hard deposits on your teeth is called “scaling.” This can be done either by using hand-held scalers or by newer technology: ultrasonic power scalers.
Ultrasonic scalers are used to remove calculus rapidly from the tooth surface. The scaling tip vibrates in the ultrasonic range of 20-45 kHz (i.e. 20,000 to 45,000 times per second), with an optimum frequency between 18 kHz and 32kHz.
Most of the scaling power is available at the tip, which is cooled with a jet of water.
There are three basic types – magnetostrictive, piezo-electric and Odontoson.
 Orthodontics is a best mutispeciality cosmetic dentistry in nagpur that is concerned with the treatment of mal-aligned teeth or malocclusions (improper bites), which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both. Early intervention of correction of teeth can prevent future dental problems.
Orthodontics is a best mutispeciality cosmetic dentistry in nagpur that is concerned with the treatment of mal-aligned teeth or malocclusions (improper bites), which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both. Early intervention of correction of teeth can prevent future dental problems.
Orthodontic treatment can focus on dental displacement only, or can deal with the control and modification of facial growth. In the latter case it is better defined as “dentofacial orthopedics”. Orthodontic treatment can be carried out for purely aesthetic reasons—improving the general appearance of patients’ teeth and face for cosmetic reasons—but treatment is often prescribed for practical reasons, providing the patient with a functionally improved bite (occlusion).
Orthodontics can be done for both children and adults. The treatment duration for correction of mal aligned teeth will take about 12 months to 18 months. You need to meet us once a month during the treatment duration.
 Tooth replantation is the reinsertion and splinting of a tooth that has been avulsed (knocked or torn out) of its socket.
Tooth replantation is the reinsertion and splinting of a tooth that has been avulsed (knocked or torn out) of its socket.
Reimplantation refers to the insertion and temporary fixation of a completely or partially avulsed (knocked out) tooth due to traumatic injury. There is no realistic way to prevent the avulsion of teeth as it usually occurs due to an accident. However, wearing a mouth guard during sports activities usually helps reduce risk.
The most common teeth to be knocked out are the upper front permanent teeth, although primary teeth can also be avulsed. Reimplantation of primary teeth is not usually performed as these teeth are naturally replaced by permanent teeth later in life.
The success of reimplantation depends on the amount of time the tooth is out of the socket. If reimplantation can be performed within one hour of the tooth being knocked out, success rates are much higher.
 Whitening is a cosmetic procedure to improve the shade of the teeth and it removes pigments and stains from the uppermost layer of the tooth or enamel to give whiter teeth. It does not involve cleaning the gums.
Whitening is a cosmetic procedure to improve the shade of the teeth and it removes pigments and stains from the uppermost layer of the tooth or enamel to give whiter teeth. It does not involve cleaning the gums.
It might lead to a limited period of sensitivity because of the ingredient used to whiten teeth, but this subsides eventually. Most people do not experience any sensitivity issues unless already present.
 Periodontics is that branch and specialty of dentistry concerned with the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the supporting and surrounding tissues of the teeth and the maintenance of the health, function and aesthetics of these structures and tissues.
Periodontics is that branch and specialty of dentistry concerned with the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and conditions of the supporting and surrounding tissues of the teeth and the maintenance of the health, function and aesthetics of these structures and tissues.
Gum or gingival diseases or periodontal disease is caused due to infection or inflammation of the gums. Untreated gum disease will affect the bone causing tooth mobility . Gum diseases can be treated by ultrasonic scaling or cleaning of the teeth, periodontal flap surgery, root planning and bone grafting procedures. The ultrasonic cleaning can be done in 1 or 2 visits. The number of visits for the periodontal flap surgery depends on the extent of the gum disease. The flap surgery are usually done under local anesthesia or under conscious sedation.
 A ceramic laminate is a thin layer of tooth colored material placed over a tooth surface, either to improve the aesthetics of a tooth, or to protect a damaged tooth surface. A composite veneer may be directly placed (built-up in the mouth), or indirectly fabricated in a dental laboratory, and later bonded to the tooth.
A ceramic laminate is a thin layer of tooth colored material placed over a tooth surface, either to improve the aesthetics of a tooth, or to protect a damaged tooth surface. A composite veneer may be directly placed (built-up in the mouth), or indirectly fabricated in a dental laboratory, and later bonded to the tooth.
Multiple veneers and laminates can close these spaces, lengthen teeth that have been shortened by wear, fill the black triangles between teeth caused by gum recession, provide a uniform color, shape, and symmetry, making teeth appear naturally beautiful and well aligned
 Dental Implants are artificial tooth roots. Holes are made into the jaw bones and the artificial roots are placed and covered over. The implants then heal and integrate with the jaw. After healing an artificial tooth is placed into the implant which functions as a natural tooth in all three aspects fulfilling the function, esthetics and physiology.
Dental Implants are artificial tooth roots. Holes are made into the jaw bones and the artificial roots are placed and covered over. The implants then heal and integrate with the jaw. After healing an artificial tooth is placed into the implant which functions as a natural tooth in all three aspects fulfilling the function, esthetics and physiology.
Dental implant has revolutionized the dentistry by compensating the long awaited proper treatment in dental field. It has proven a success rate of over 95%. So almost it is an ideal solution for a missing tooth.
Single tooth implant replaces a missing tooth. Holes are made into the jaw bones and the artificial roots are placed and covered over. The implants then heal and integrate with the jaw. After healing an artificial tooth is placed into the implant which functions as a natural tooth in all three aspects fulfilling the function, esthetics and physiology.
It is a quick process of replacing a missing tooth. It can be finished within an hour, so patient leaves the clinic with replaced missing teeth in single visit. Additional visit required for placement of permanent crown and follow up.
Six implants in each arch is placed so total twelve implants are used to framework the bridge work providing full mouth teeth replacement. This setup work as close to natural teeth.
Patients who have dental implants report the following benefits:
- Better ability to chew
- Improved appearance
- Be more confident
- Maintain a healthier diet
- Are happier and feel better about themselves.
Hospital Facilities
 A bone graft is a surgical procedure used to fix problems with bones or joints. Bone grafting, or transplanting of bone tissue, is beneficial in fixing bones that are damaged from trauma, or problem joints. It’s also useful for growing bone around an implanted device, such as a total knee replacement. A bone graft may fill a void where bone is absent or help provide structural stability.
A bone graft is a surgical procedure used to fix problems with bones or joints. Bone grafting, or transplanting of bone tissue, is beneficial in fixing bones that are damaged from trauma, or problem joints. It’s also useful for growing bone around an implanted device, such as a total knee replacement. A bone graft may fill a void where bone is absent or help provide structural stability.
The bone used in a bone graft can come from your body, a donor, or it can be entirely man-made. The bone graft can provide a framework where new, living bone can grow if it’s accepted by the body.
 The two most common types of bone grafts are:
The two most common types of bone grafts are:
- An allograft uses bone from a deceased donor or a cadaver that has been cleaned and stored in a tissue bank.
- An autograft comes from a bone inside your body, such as your ribs, hips, pelvis, or wrist.
The type of graft used depends on the type of injury your surgeon will be repairing. Allografts are commonly used in hip, knee, or long bone reconstruction. Long bones include arms and legs. The advantages are there’s no additional surgery needed to acquire the bone. It also lowers your risk of infection since additional incisions or surgery aren’t required.
 Bone grafting is done for numerous reasons, including injury and disease. There are four main reasons bone grafts are used:
Bone grafting is done for numerous reasons, including injury and disease. There are four main reasons bone grafts are used:
- A bone graft may be used in the case of multiple or complex fractures or those that don’t heal well after initial treatment.
- Fusion helps two bones heal together across a diseased joint. Fusion is most often done on the spine.
- Regeneration is used for bone lost to disease, infection, or injury. This can involve using small amounts of bone in bone cavities or large sections of bones.
- A graft can be used to help bone heal around surgically implanted devices, like joint replacements, plates, or screws.
 Facial Bone & Jaw Fracture can be complex and multi-specialty involvement in their management may be needed. Injury can involve the skin and soft tissues as well as resulting in fractures. Acute and long-term psychological problems can result from maxillofacial trauma and disfigurement.[1][2] The first human face allograft was successfully performed in 2006 in France and has potential for use in facial reconstructive surgery secondary to maxillofacial trauma.
Facial Bone & Jaw Fracture can be complex and multi-specialty involvement in their management may be needed. Injury can involve the skin and soft tissues as well as resulting in fractures. Acute and long-term psychological problems can result from maxillofacial trauma and disfigurement.[1][2] The first human face allograft was successfully performed in 2006 in France and has potential for use in facial reconstructive surgery secondary to maxillofacial trauma.
The maxillofacial region can be divided into three parts:
- The upper face – the frontal bone and frontal sinus.
- The midface – the nasal, ethmoid, zygomatic and maxillary bones.
- The lower face – the mandible.
 The region of the orbit:
The region of the orbit:
- The superior orbital margin is formed by the frontal bone.
- The lateral orbital margin is formed by the frontal process of the zygoma, the zygomatic process of the frontal bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid bone.
- The inferior orbital margin is formed by the maxilla and the zygoma.
- The medial orbital margin is formed by the frontal process of the maxilla, the lacrimal bone, the angular and orbital process of the frontal bone and the ethmoid bone.
- The orbital floor is formed by the roof of the maxillary sinus.
- Parts of the sphenoid, palatine and ethmoid bones form the apex of the orbit.
Blood and sensory supply:
- Branches of the external carotid artery supply blood to the face.
- The facial nerve supplies the muscles of facial expression.
- The ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular branches of the trigeminal nerve supply sensation to the skin of the face.
This is usually caused by:
- Assault (most common; domestic violence is an important cause; alcohol may be involved).[6]
- Road traffic accidents (midface fractures can occur).
- Falls.
- Sporting accidents.
 Oral cancer appears as a growth or sore in the mouth that does not go away. Oral cancer, which includes cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and pharynx (throat), can be life threatening if not diagnosed and treated early.
Oral cancer appears as a growth or sore in the mouth that does not go away. Oral cancer, which includes cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and pharynx (throat), can be life threatening if not diagnosed and treated early.
 The most common symptoms of oral cancer include:
The most common symptoms of oral cancer include:
- Swellings/thickenings, lumps or bumps, rough spots/crusts/or eroded areas on the lips, gums, or other areas inside the mouth
- The development of velvety white, red, or speckled (white and red) patches in the mouth
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
- Unexplained numbness, loss of feeling, or pain/tenderness in any area of the face, mouth, or neck
- Persistent sores on the face, neck, or mouth that bleed easily and do not heal within 2 weeks
- A soreness or feeling that something is caught in the back of the throat
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing, speaking, or moving the jaw or tongue
- Hoarseness, chronic sore throat, or change in voice
- Ear pain
- A change in the way your teeth or dentures fit together
- Dramatic weight loss
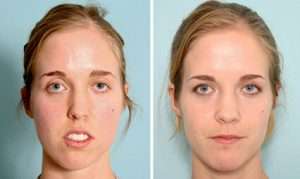
 Corrective jaw, or orthognathic surgery is performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon (OMS) to correct a wide range of minor and major skeletal and dental irregularities, including the misalignment of jaws and teeth. Surgery can improve chewing, speaking and breathing. While the patient’s appearance may be dramatically enhanced as a result of their surgery, orthognathic surgery is performed to correct functional problems.
Corrective jaw, or orthognathic surgery is performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon (OMS) to correct a wide range of minor and major skeletal and dental irregularities, including the misalignment of jaws and teeth. Surgery can improve chewing, speaking and breathing. While the patient’s appearance may be dramatically enhanced as a result of their surgery, orthognathic surgery is performed to correct functional problems.

Following are some of the conditions that may indicate the need for corrective jaw surgery:
- Difficulty chewing, or biting food
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chronic jaw or jaw joint (TMJ) pain and headache
- Excessive wear of the teeth
- Open bite (space between the upper and lower teeth when the mouth is closed)
- Unbalanced facial appearance from the front, or side
- Facial injury
- Birth defects
- Receding lower jaw and chin
- Protruding jaw
- Inability to make the lips meet without straining
- Chronic mouth breathing
- Sleep apnea (breathing problems when sleeping, including snoring)
 Your salivary glands produce saliva, which keeps your mouth moist, helps protect your teeth from rapid decay, and helps you to digest your food. The salivary glands are relatively small, and they’re around the inner linings of your mouth, lips, and cheeks.
Your salivary glands produce saliva, which keeps your mouth moist, helps protect your teeth from rapid decay, and helps you to digest your food. The salivary glands are relatively small, and they’re around the inner linings of your mouth, lips, and cheeks.
The symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- a painful lump under the tongue
- pain that increases when eating
Sialadenitis symptoms include:
- a lump in your cheek or under your chin
- pus that drains into your mouth
- strong or foul-smelling pus
- a fever
Cysts that grow in your salivary glands can cause:
- yellow mucus that drains upon bursting
- difficulty eating
- difficulty speaking
- difficulty swallowing
Viral infections in the salivary glands, such as mumps, can cause:
- fever
- muscle aches
- joint pain
- swelling on both sides of the face
- headache

The symptoms of Sjogren’s syndrome include:
- dry mouth
- dry eyes
- tooth decay
- sores in the mouth
- joint pain or swelling
- dry cough
- unexplained fatigue
- swollen salivary glands
- frequent salivary gland infections
If you have diabetes or alcoholism, you may also have swelling in the salivary glands.
If you notice the following symptoms, see your doctor:
- a bad taste in your mouth
- dry mouth
- mouth pain
- facial swelling
- trouble opening your mouth
A number of diseases can affect your salivary glands. These range from cancerous tumors to Sjogren’s syndrome. While some go away with time or antibiotics, others require more serious treatments, including surgery.
 Temporomandibular joint is a hinge that connects your jaw to the temporal bones of your skull, which are in front of each ear. It lets you move your jaw up and down and side to side, so you can talk, chew, and yawn.
Temporomandibular joint is a hinge that connects your jaw to the temporal bones of your skull, which are in front of each ear. It lets you move your jaw up and down and side to side, so you can talk, chew, and yawn.
Problems with your jaw and the muscles in your face that control it are known as temporomandibular disorders (TMD). But you may hear it wrongly called TMJ, after the joint.
Causes:
Injury to your jaw, the joint, or the muscles of your head and neck — like from a heavy blow or whiplash — can lead to TMD. Other causes include:
- Grinding or clenching your teeth, which puts a lot of pressure on the joint
- Movement of the soft cushion or disc between the ball and socket of the joint
- Arthritis in the joint
- Stress, which can cause you to tighten facial and jaw muscles or clench the teeth
Common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness in your face, jaw joint area, neck and shoulders, and in or around the ear when you chew, speak, or open your mouth wide
- Problems when you try to open your mouth wide
- Jaws that get “stuck” or “lock” in the open- or closed-mouth position
- Clicking, popping, or grating sounds in the jaw joint when you open or close your mouth or chew. This may or may not be painful.
- A tired feeling in your face
- Trouble chewing or a sudden uncomfortable bite — as if the upper and lower teeth are not fitting together properly
- Swelling on the side of your face
 Cleft lip and cleft palate are facial and oral malformations that occur very early in pregnancy, while the baby is developing inside the mother. Clefting results when there is not enough tissue in the mouth or lip area, and the tissue that is available does not join together properly.
Cleft lip and cleft palate are facial and oral malformations that occur very early in pregnancy, while the baby is developing inside the mother. Clefting results when there is not enough tissue in the mouth or lip area, and the tissue that is available does not join together properly.
A cleft lip is a physical split or separation of the two sides of the upper lip and appears as a narrow opening or gap in the skin of the upper lip. This separation often extends beyond the base of the nose and includes the bones of the upper jaw and/or upper gum.
 A cleft palate is a split or opening in the roof of the mouth. A cleft palate can involve the hard palate (the bony front portion of the roof of the mouth), and/or the soft palate (the soft back portion of the roof of the mouth).
A cleft palate is a split or opening in the roof of the mouth. A cleft palate can involve the hard palate (the bony front portion of the roof of the mouth), and/or the soft palate (the soft back portion of the roof of the mouth).
Cleft lip and cleft palate can occur on one or both sides of the mouth. Because the lip and the palate develop separately, it is possible to have a cleft lip without a cleft palate, a cleft palate without a cleft lip, or both together.
 An impacted tooth is a tooth that gets blocked as it is pushing through the gum into your mouth (erupting). Wisdom teeth often are impacted.
An impacted tooth is a tooth that gets blocked as it is pushing through the gum into your mouth (erupting). Wisdom teeth often are impacted.
Wisdom teeth usually begin to come in between the ages of 17 and 21. Dentists call these teeth third molars. They may become impacted because there’s not enough room in your mouth for them. A wisdom tooth also might be trying to come in sideways. Or, it might be tilted in your jaw.
An impacted tooth can be painless. You may not even realize it’s there. However, when an impacted wisdom tooth tries to come in, the flap of gum on top of it can become infected and swollen. This can hurt. You might even feel pain in nearby teeth, or in the ear on that side of your face.
 An impacted tooth can lead to an infection called pericoronitis. If untreated, this infection can spread to the throat or into the neck. Severe infections require a hospital stay and surgery.
An impacted tooth can lead to an infection called pericoronitis. If untreated, this infection can spread to the throat or into the neck. Severe infections require a hospital stay and surgery.
Impacted teeth also can get cavities. An impacted tooth can push on the neighboring molar. This can lead to tooth movement, decay or gum disease. It also can change the way your teeth come together. Rarely, impacted teeth can cause cysts or other growths in the jaw.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Swelling of the gum in the back of your mouth
- Difficulty opening your jaw
- Bad breath
- A bad taste in the mouth
- Pain when you open your mouth
- Pain when chewing or biting
 Pain can occur for several days and then disappear. It can come back weeks or months later.
Pain can occur for several days and then disappear. It can come back weeks or months later.
Diagnosis
Your dentist will examine the area. If necessary, he or she will take X-rays. X-rays can show where your wisdom teeth are and if they are impacted.
Expected Duration
When the tooth is taken out, the symptoms will go away.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent an impacted tooth. You can prevent cavities by brushing and flossing.
Treatment
You can sometimes relieve minor irritation by rinsing with warm salt water (1/2 teaspoon of salt in 8 ounces of water). Over-the-counter pain relievers also may help.
If the tooth continues to cause pain, is infected or interferes with nearby teeth, the usual treatment is to take it out. Extracting one tooth can take 5 to 30 minutes, depending on where it is. In some cases, an infection requires antibiotics.
Patients are often referred to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon to have an impacted tooth removed. Before removing the tooth, your dentist or surgeon will discuss the procedure and the type of anesthesia and sedatives he or she will use. You will not be able to eat for six hours before surgery. If you take any medicines, keep on schedule with them. Someone should drive you to the appointment and drive you home.
After the surgery you may have swelling of the cheeks and jaw. It may be hard to eat certain foods. Follow your dentist’s or surgeon’s instructions carefully for the best recovery. Complications of surgery are rare, but do occur.
An impacted tooth may not bother you or affect nearby teeth. In this case, you won’t need immediate treatment. However, your dentist probably will recommend that the tooth be taken out to avoid future problems.
Many people have all four of their wisdom teeth taken out at once. Sometimes this surgery is done before the teeth have started coming in. This prevents future problems. This usually is done in an oral and maxillofacial surgeon’s office with sedation and local anesthesia. Often, it is better to have your wisdom teeth taken out before you turn 21. The surgery usually is less complicated. The tissue and bone also heal better.
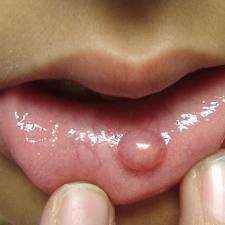 Tumors and cysts are two distinct entities.
Tumors and cysts are two distinct entities.
- Cyst. A cyst is a sac that may be filled with air, fluid or other material. A cyst can form in any part of the body, including bones, organs and soft tissues. Most cysts are noncancerous (benign). Although cancers can form cysts.
Some common examples of cysts include sebaceous (epidermoid) cysts — small bumps that form just beneath the skin — cysts that occur in the liver (hepatic), cysts that occur in the kidneys (renal), and breast and ovarian cysts. It’s important to note, however, that nearly all cancers are capable of producing cysts.
- Tumor. A tumor is any abnormal mass of tissue or swelling. Like a cyst, a tumor can form in any part of the body. A tumor can be benign or cancerous (malignant).
 Cysts that appear uniform after examination by ultrasound or a computerized tomography (CT) scan are almost always benign and should simply be observed. If the cyst has solid components, it may be benign or malignant and should have further evaluation. The best test to determine whether a cyst or tumor is benign or malignant is to take a sample of the affected tissue — or, in some cases, the entire suspicious area — by removing it and studying it under a microscope. This is known as a biopsy.
Cysts that appear uniform after examination by ultrasound or a computerized tomography (CT) scan are almost always benign and should simply be observed. If the cyst has solid components, it may be benign or malignant and should have further evaluation. The best test to determine whether a cyst or tumor is benign or malignant is to take a sample of the affected tissue — or, in some cases, the entire suspicious area — by removing it and studying it under a microscope. This is known as a biopsy.
